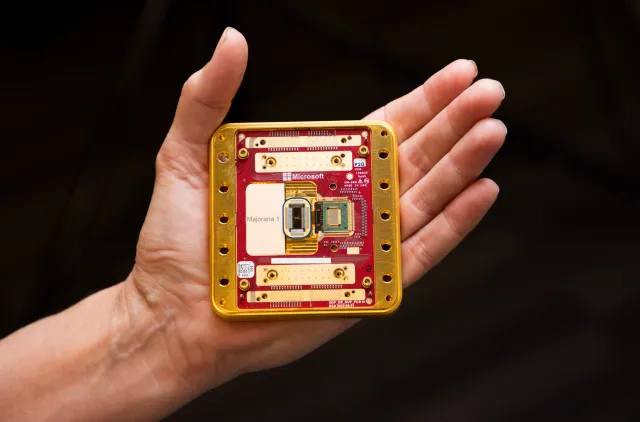
Microsoft has spent 17 years researching a new material and architecture for quantum computing.
Quantum computing has long been hailed as the next frontier in technological innovation, promising to revolutionize industries ranging from healthcare to materials science. After nearly two decades of relentless research and development, Microsoft has announced a major milestone in this journey: the unveiling of its first quantum processor, Majorana 1. Built on a groundbreaking new architecture, this processor could pave the way for scalable, fault-tolerant quantum computing, unlocking solutions to some of the world’s most complex problems.
A 17-Year Pursuit of Quantum Excellence
For 17 years, Microsoft has been investing heavily in quantum research, working towards creating a viable quantum computing system capable of solving industrial-scale problems. The centerpiece of this effort is Majorana 1, a processor that promises to overcome one of the biggest challenges in quantum computing: the stability of qubits.
Unlike classical computers that rely on binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers use qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to the principles of superposition and entanglement. However, qubits are notoriously fragile, highly sensitive to noise, and prone to errors, making it difficult to scale quantum computers. Microsoft’s new approach aims to change that.
The Majorana Breakthrough: A Million Qubits on a Single Chip
What sets Majorana 1 apart is its ability to potentially fit one million qubits onto a single chip, roughly the size of the CPUs found in today’s desktop computers and servers. Instead of using conventional electron-based qubits, Microsoft has turned to an exotic particle first theorized by Italian physicist Ettore Majorana in 1937.
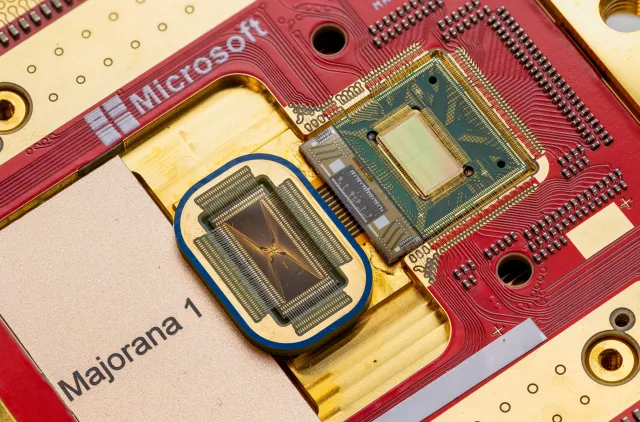
To harness the power of Majorana particles, Microsoft has pioneered the development of what it calls the world’s first topoconductor—a revolutionary new material that not only enables the observation of Majorana particles but also allows them to be controlled for computational purposes. This breakthrough paves the way for creating more reliable and scalable qubits, addressing one of the fundamental obstacles in quantum computing.
The Science Behind the Innovation
Microsoft’s research findings were published in the prestigious journal Nature, detailing the journey toward developing topological qubits. The key to this advancement lies in the creation of a novel material composed of indium arsenide and aluminum, which has allowed Microsoft to construct eight topological qubits on a single chip. The ultimate goal? To scale this architecture to a system containing one million qubits.
A quantum computer of this magnitude could perform simulations with unprecedented accuracy, leading to groundbreaking discoveries in medicine, materials science, artificial intelligence, cryptography, and beyond. The potential applications of such a system are limitless, as quantum computing has the power to process vast amounts of data and solve equations that would take traditional supercomputers centuries to complete.
Microsoft’s Quantum Team: Engineering the Future
The journey toward a fully scalable quantum computer has been spearheaded by some of the brightest minds at Microsoft. Zulfi Alam, Corporate Vice President of Quantum at Microsoft, emphasized the significance of this milestone:
“Our leadership has been working on this program for the last 17 years. It’s the longest-running research program in the company. After 17 years, we are showcasing results that are not just incredible—they’re real. They will fundamentally redefine how the next stage of the quantum journey takes place.”
Alam, who previously worked on Microsoft’s HoloLens project, has leveraged advanced fabrication techniques to accelerate the company’s quantum ambitions. Alongside him is Chetan Nayak, a Microsoft Technical Fellow, who highlighted the strategic approach that led to this breakthrough:
“We took a step back and asked, ‘What does the transistor for the quantum age need to look like?’ That’s how we arrived at this solution—it’s the precise combination, quality, and intricate details of our new materials stack that have enabled a new kind of qubit and, ultimately, a scalable architecture.”
A Quantum Future in Sight: Microsoft’s Partnership with DARPA
In recognition of its groundbreaking work, Microsoft has been selected by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) as one of two companies to advance to the final phase of its Underexplored Systems for Utility-Scale Quantum Computing (US2QC) program. This selection cements Microsoft’s position as a leader in the race toward scalable quantum computing.
The next step? Microsoft will focus on building a fault-tolerant prototype quantum computer using its topological qubit architecture. And rather than taking decades, the company expects to accomplish this within years—a timeline that significantly accelerates the realization of practical quantum applications.
The Road Ahead: Unlocking Real-World Applications
Microsoft’s quantum breakthrough is more than just a scientific milestone—it’s a gateway to solving real-world challenges. A million-qubit quantum computer could drive innovation in fields such as:
- Pharmaceuticals & Drug Discovery: Simulating molecular interactions at an atomic level to accelerate the development of new treatments and vaccines.
- Climate Science: Enhancing climate modeling and discovering new materials for clean energy solutions.
- Cybersecurity: Developing ultra-secure cryptographic methods resistant to traditional hacking techniques.
- Artificial Intelligence: Enabling AI models to process and learn from data at an unprecedented scale.
- Finance & Optimization: Solving complex optimization problems that could revolutionize supply chain logistics and financial modeling.
A Defining Moment in Quantum Computing
Microsoft’s unveiling of Majorana 1 marks a defining moment in the quest for practical and scalable quantum computing. With its breakthrough topoconductor material, the company has laid the foundation for a fault-tolerant quantum future—one that could reshape industries, redefine computational limits, and push the boundaries of scientific discovery.
As the company moves forward with its DARPA-backed prototype, the quantum revolution is no longer a distant dream. The age of scalable quantum computing is on the horizon, and Microsoft is leading the charge toward a new era of technological possibility.
Stay tuned as we continue to follow Microsoft’s quantum journey and its potential impact on the world. The future is quantum, and it’s happening now.